A
AA – Accelerated Aging
Storage of samples at an elevated temperature in order to simulate real-time aging in a reduced amount of time.
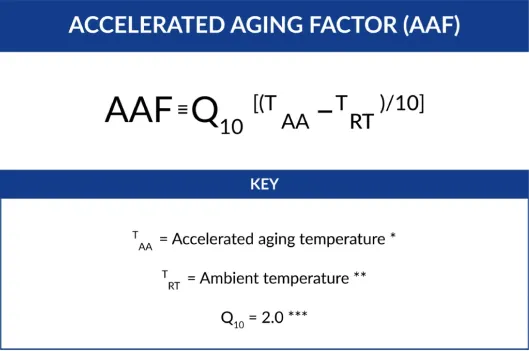
AAF – Accelerated Aging Factor
An estimated ratio of the time needed to achieve the same level of physical property change as a sterile barrier system stored at real time conditions.
AB – Accredited Body
AFAP – Risk reduced As Far As Possible
AL – Assurance Level
AL – Assurance Load
ASR- American Systems Register
ASTM D4169
Standard Practice for Performance Testing of Shipping Containers and Systems. This practice provides a uniform basis of evaluatin–, in a laboratory-- the ability of shipping units to withstand the distribution environment. This is accomplished by subjecting them to a test plan consisting of a sequence of anticipated hazard elements encountered in various distribution cycles.
Attribute Testing
Attribute testing results in a ‘pass/fail’ determination and does not provide numerical output. Bubble leak testing and visual inspection are examples of attribute testing because they result in a pass/fail.
B
B/F – Bacteriostasis Fungistasis
BA – Broadly Acceptable Risk
BET – Bacterial Endotoxin – uses LAL
BI – Biological Indicator
During sterilization, to test whether the EO completely sterilized the shipper, the BI is marked to show there is a bio-organism that should be sterilized by EO. A box will usually be indicated (on a specific side of the box) with a label identifying the control sample in the sterilization test.
BL – Bubble Leak
BOM – Bill Of Material
Bubble Leak Testing
ASTM F2096 Standard Test Method for Detecting Gross Leaks in Packaging by Internal Pressurization. This test method can detect gross leaks in packaging as small as 250 microns. The package is inflated under water to a predetermined pressure and is observed for a steady stream of air bubbles that would indicate a failure.
Burst Strength Testing
ASTM F1140 Standard Test Method for Internal Pressurization Failure Resistance of Unrestrained Packages. The test methods within this standard increasingly pressurizes the package until it fails. These test methods provide a rapid means of evaluating tendencies for package failure when the package is exposed to a pressure differential.
C
CA/PA – Corrective Action / Preventative Action
CAB – Conformity Assessment Body
CAR – Corrective Action Report
CD – Critical Dimension (circled)
CD – Cross Direction
CFR – Code of Federal Regulation
CFU – Colony Forming Units
Class I Medical Device
Low risk device i.e. bandages
*The EU has similar classes of severity with Class I as the lowest risk
Class II Medical Device
Intermediate-risk devices
*The EU has similar classes of severity with Class I as the lowest risk
Class III Medical Device
High-risk devices (that sustain life i.e. cardiovascular devices)
*The EU has similar classes of severity with Class I as the lowest risk
CM – Contract Manufacturer
COD – Certification Of Destruction
CompliancePack™
or CPack™, is PCL’s ISO 11607-compliant pre-validated packaging platform.
CS – Component Specification
CSR – Cellulose-based wrapping material i.e. CSR wrap
CV – Cleaning Validation
D
DFMEA – Design Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
DHF – Device History Files
DHR – Device History Records (Master list)
DL – Dye Leak
DOE – Design Of Engineering/Experiment
DOT – Hazardous Material Qualification
DV – Design Verification (Transit)
DW – Double Wall
Dye Leak Testing / Dye Pen
ASTM F1929 Standard Test Method for Detecting Seal Leaks in Porous Medical Packaging by Dye Penetration. This test method detects breaches as small as 50 microns in a package seal edge. A dye solution is applied to the seal to be tested for leaks.
E
ECT – Edge Crush Test
eIFU – electronic Instruction for Use
Environmental Conditioning
ASTM D4332 Standard Practice for Conditioning Containers, Packages, or Packaging Components for Testing. This practice provides standard and special conditioning and testing atmospheres that may be used to simulate particular field conditions that a container, package, or packaging component may encounter during its life or testing cycle.
EO – Ethelene Oxide sterilization
EOI – Equipment Operating Instructions
ERP – Enterprise Resource Planning (NetSuite)
EU – Endotoxin Units
F
FAI – First Article Inspection
FEAS – Feasibility
FG – Finished Good
FIC – Formal Information Collection
G
GA – Gage
GLP – Good Laboratory Practice
GMP – Good Manufacturing Practice
GRMS – Gravity Root Mean Square (unit of measure)
GS1 – General Specifications (Barcode reading)
GTIN – Global Trade Item Number
I
IFU – Instruction for Use
ILS – Inter-Laboratory Studies
INT – Risk Intolerable
IOPP – Institute of Packaging Professionals
IP – Inspection Plan
IQ – Installation Qualification
ISO – International Organization of Standards
ISO 11607: International Standard for Packaging Terminally Sterilized Medical Devices
This document specifies requirements for the design of sterile barrier systems for terminally sterilized medical devices, the basic attributes required of materials, and design validation requirements.
ISO 13485
International Standard for Medical Devices – Quality management systems – requirements for regulatory purposes. This standard ensures consistent design, development, production, installation, and delivery of medical devices.
ISTA – International Safe Transit Association
ITM – Internal Test Method
L
Label Adhesion
ASTM D3330 Standard Test Method for Peel Adhesion of Pressure Sensitive Tape. This test method covers the measurement of the peel adhesion of pressure-sensitive tape. It provides a means of assessing the uniformity of the adhesion of sensitive tape.
LAL – Limulus Amebocyte Lysate
LB – Label Specification
LOA – Level of Assurance
LOD – Limit Of Detection
LOI – Laboratory Operating Instruction
LOQ – Limit Of Qualification
LS – Labeling Spec
LSL – Lower Spec Limit
M
MD – Machine Direction
MDM – Medical Device Manufacturer
MDMA – Medical Device Manufacturer Association
MDPTC – Medical Device Packaging Technical Committee
MVTR – Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate
N
NC – Non-Conformance
Nom – Nominal
Non-Attribute Testing
Non-attribute testing provides an output that has a value. For example, peel strength testing pulls apart the two pieces of material that make a seal and outputs a value.
NPD – New Product Development
O
OEM – Original Equipment Manufacturer
OQ – Operation Qualification
OTR- Over The Road
P
Packaging Compliance Medical (PCM)
An ISO 13485:2016 certified contract manufacturer (CM) that specializes in small-volume production.
PCL – Packaging Compliance Labs
PCM – Packaging Compliance Medical
PEEK – Polyetheretherketone
Peel Strength Testing
ASTM F88 Standard Test Method for Seal Strength of Flexible Barrier Systems. Peel strength testing measures the strength of seals on rigid and flexible materials.
PFMEA – Process Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
PN – Part Number
PO – Purchase Order
PQ – Performance Qualification
Process Validation
A process validation verifies that equipment operates as intended. This includes ensuring that the sealing and forming processes are repeatable and reliable.
PSI – Pounds per Square Inch
PV – Process Verification
Q
QMS – Quality Management System
QR – Quick Response
R
RPN – Risk Priority Number (i.e. Severity x Probability = RPN)
RT – Router
RTA – Real Time Aging
Storage time of samples at ambient conditions.
RW – Rework
S
SAL – Sterility Assurance Level
SBS – Sterile Barrier System
SCAR – Supplier Corrective Action Requests
Shelf Life Validation
Shelf life testing (also known as stability or aging) testing demonstrates the ability of the packaging system to maintain sterile integrity and other key performance properties over time.
SIP – Sample Item Portion
SKU – Shop Keeping Unit
SLV – Shelf-Life Validation
SME – Subject Matter Expert
SN – Study Number
SS – Seal Strength
Sterile barrier package integrity / Sterile barrier system integrity
Testing that establishes the capability of the sterile barrier system to maintain sterility.
Sutherland Rub
ASTM D5264 Standard Practice for Abrasion Resistance of Printed Materials by the Sutherland Rub Tester. This test method determines the abrasion resistance of printed materials (such as labels, carton boxes, inserts, and other packaging materials) that have graphics printed on a flat substrate.
SV – Sterile Validation
SW – Seal Width
SW – Single Wall
T
TL – Tooling
TMI – Test Method Introduction
TMV – Test Method Validation
TOC – Total Organic Carbon
TOPS – Total Optimization Packaging Software
TPS – Test Parameter Sheet
TPU – Thermoplastic Polyurethane
Transit Validation
Transit testing challenges the packaging system’s ability to withstand the forces of sterilization, handling, and distribution while maintaining a sterile barrier and other important characteristics.
U
UDI – Unique Device Identifier
Underwater Vacuum Leak
ASTM D3078 Standard Test Method for Determination of Leaks in Flexible Packaging by Bubble Emission. This test method covers the determination of gross leaks in packaging containing a headspace gas.
Usability Evaluation
ISO 11607-1 was updated to include Usability Evaluation for Aseptic Presentation (section 7). This revision requires medical device manufacturers to assess their sterile barrier system designs while considering healthcare professional inputs.
USL – Upper Spec Limit
USP – United States Pharmacopeia
V
VIS – Visual Inspection
Visual Inspection Testing
ASTM F1886 Standard Test Method for Determining Integrity of Seals for Flexible Packaging by Visual Inspection. This test method provides a qualitative visual inspection method to evaluate the appearance characteristics of unopened, intact seals to identify defects that could affect the integrity of the package.
VOE – Verification of Effectiveness
W
WFI – Water For Injection
WI – Work Instruction
WIP – Work In Progress
WO – Work Order
